Self-administration of Subcutaneous Injections: A Guide
In the comfort of your own home, giving yourself a subcutaneous injection can be a manageable task with the right preparation and knowledge. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you navigate this process safely and effectively.
## Preparation
Before you begin, gather essential materials such as alcohol wipes, sterile 2 x 2 gauze pads, a new needle and syringe of the correct size, disposable gloves (if available), and medication prepared according to your healthcare provider's instructions or the medication's packaging.
## Choosing the Injection Site
Approved injection sites include the abdomen (at least two inches away from the belly button), buttocks, front of the thigh, and outer upper arm (if a caregiver is administering). To prevent skin changes or scars, rotate sites, ensuring injections are at least one inch apart.
## Administering the Injection
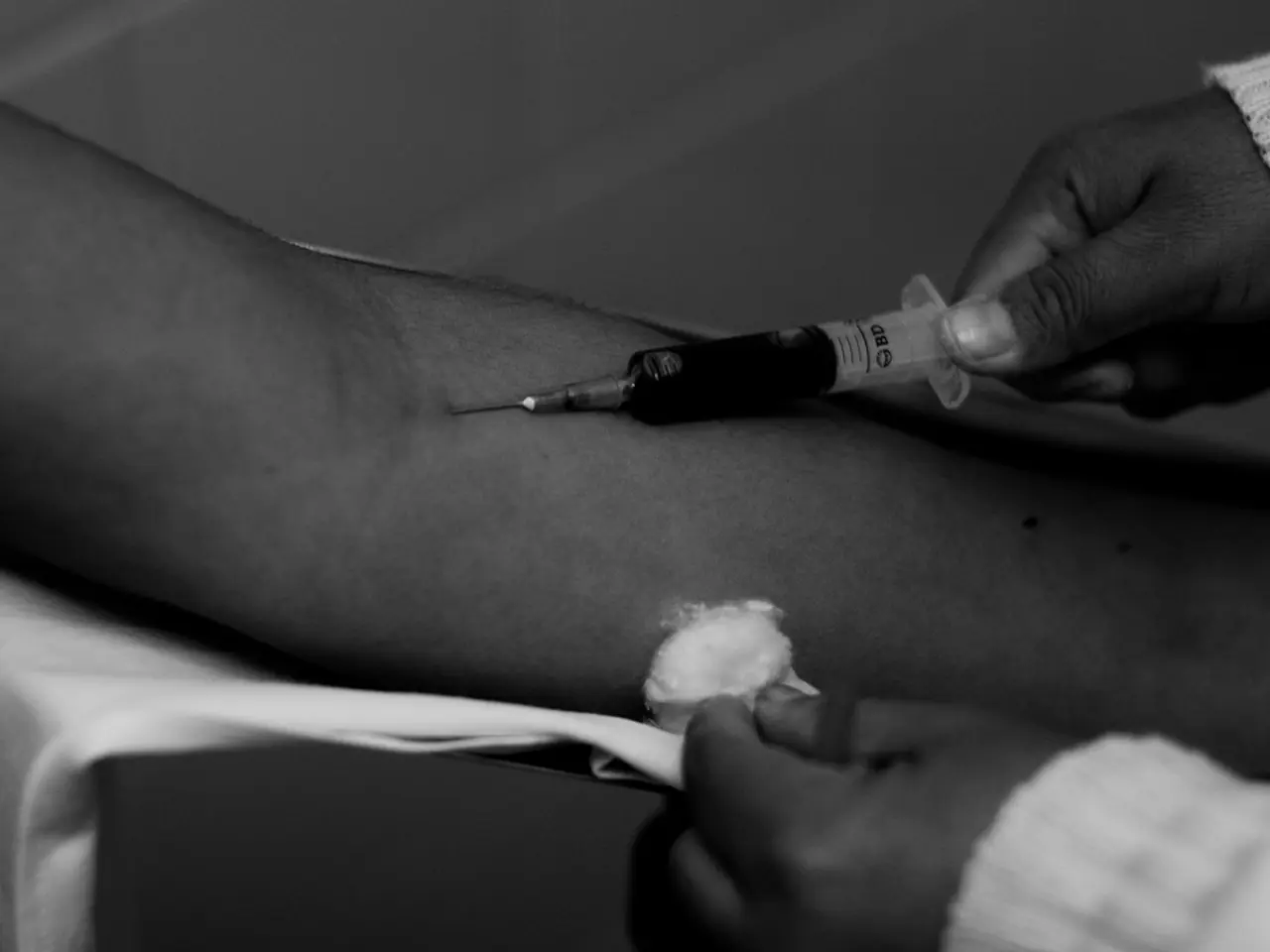
1. Clean the Area: Use an alcohol wipe to clean the injection site, allowing it to dry completely before proceeding. 2. Pinch the Skin: Pinch at least 2 inches of skin at the chosen site. If you can only grasp 1 inch of skin, use a 45-degree angle. 3. Insert the Needle: Insert the needle straight in at a 90-degree angle for a firm grip, or at a 45-degree angle for a less firm grip. 4. Administer the Medication: Once the needle is fully inserted, slowly push the plunger to release the medication. 5. Withdraw the Needle: Remove the needle at the same angle it was inserted. 6. Apply Pressure: Gently wipe the area with a gauze pad to apply pressure and help prevent bleeding.
## Post-Injection Care
Dispose of needles and syringes in a puncture-resistant container, and follow the storage instructions provided with your medication.
## Additional Tips
- If the medication has been refrigerated, allow it to warm to room temperature before administering. - Discuss any discomfort with your healthcare provider. - Proper disposal of sharps is crucial to prevent accidental injury and the spread of infections. - Incorrect injection techniques may lead to discomfort, bruising, and improper absorption of medication. - Injections can be given in various areas of the body, including the abdomen, back of the upper arm, and front of the thigh. - Your healthcare provider will work with you to answer questions and ensure you feel comfortable with self-injection. - Registered nurse Chrystle Hoyt provides guidance on how to correctly give yourself a subcutaneous injection. - Handwashing is essential for preventing the spread of germs, and should be done for at least 20 seconds. - A spouse or family member can learn how to administer injections and support you in the process. - Subcutaneous injections can be required for a variety of conditions, such as Type 2 diabetes, allergic reactions, and administering insulin, blood thinners, fertility drugs, epinephrine, and pain medication like morphine.
Always follow specific instructions from your healthcare provider or the medication's packaging for administering subcutaneous injections. If you are unsure about any part of the process, consult with a healthcare professional for guidance.
- Gather essential materials for self-injection at home, including alcohol wipes, gauze pads, a new needle and syringe, gloves (if available), and medication prepared as instructed.
- For managing Type 2 diabetes, insulin, blood thinners, fertILITY drugs, epinephrine, pain medication, or treating certain medical-conditions, subcutaneous injections may be required.
- To ensure health and wellness, understand therapeies and treatments for chronic diseases like Type-2 diabetes, and be aware of the importance of nutrition in managing these conditions.
- Fitness and exercise, along with proper nutrition, play a significant role in maintaining overall health, and can aid in the management of chronic diseases such as Type-2 diabetes.
- Medicare can offer coverage for medical equipment, supplies, health-and-wellness programs, and certain treatments, including the management of chronic diseases like Type-2 diabetes.
- Preventing the spread of infections is crucial, so always dispose of sharps (needles and syringes) properly and practice good hand hygiene (handwashing for at least 20 seconds) to maintain a healthy lifestyle.